 Image courtesy of [changsterdam via Flickr]
Image courtesy of [changsterdam via Flickr]
Society and Culture
The New Urban America: Cities of Visitors and the Absentee Rentier Class
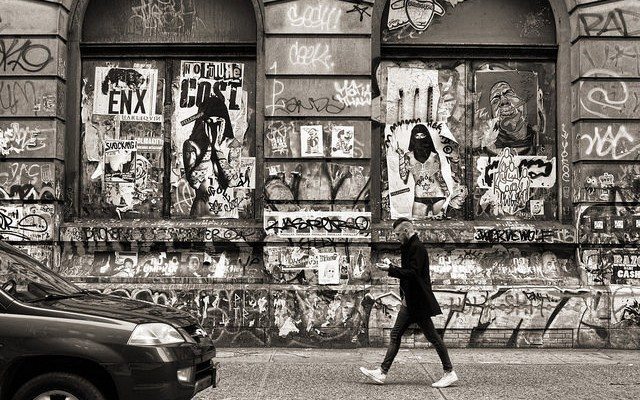
“UUGGHH.” That’s how Minneapolis-based street artist Eric Rieger, aka Hottea, responded to the latest indication of gentrification in New York. One-ninety Bowery has stood the test of time. The imposing six-story limestone Renaissance Revival relic has long been a cultural landmark. Built in 1899, then Germania Bank of New York City serviced its surrounding community, “Little Germany” (Kleindeutschland), once the largest German-American–then-bourgeois–enclave in the country.
In 1966, long after the bank dissolved, photographer Jay Maisel bought the abandoned edifice and converted its facilities into the largest single-family home in New York City. That was until Fall 2014, when Maisel reluctantly sold his spacious dwelling to one of the most voracious real-estate developers swallowing up NYC properties today. RFR Holdings LLC bought the property for an undisclosed price in September, valued between $35 and 70 million, with plans to flip the building, marketing it as ideal for retailing at the base with condominiums above, and offices, or even an art gallery.

190 Bowery, courtesy of erin williamson via Flickr.

Courtesy of erin williamson via Flickr.
Should we be surprised? With the New Museum a block away, a Whole Foods Market nearby, scores of luxury apartments, boutiques, and art galleries immediately South, it was only a matter of time before 190 Bowery succumbed to SoHo, the epicenter of loft living. RFR will be responsible for the “renovation” of the building’s cultural memory, of course; developers have already issued a rendering of the facade scrubbed clean of the layers of graffiti, on which artists including Keith Haring, COST, NEKST, Shepard Fairey, and others have made their marks for the last three decades. One-ninety Bowery is “the last remaining part of ‘old New York’,” lamented Hottea. “This building is so iconic… it’s been there for years. I think it reminds a lot of people of what New York used to be, and how that’s being taken away… UUGGHH. That’s all I can say. When is it going to stop?” But such is the normal arch of the gentrification narrative, 5 Pointz being a glaring example. We should, however, be concerned with the manner in which this process is taking place.
RFR Holdings LLC was founded in 1991 by Aby Rosen and Michael Fuchs, German-born real-estate tycoons who together own 71 properties globally. Over the last year, Rosen and Fuchs have spent $250 million on Manhattan land purchases, $500 million on office building acquisitions, and nearly $150 million on retail property–a spending spree to rival that of Quicken Loans founder Dan Gilbert who now owns most the real estate in downtown Detroit. Aside from the starkly different cities in which their properties are located, Gilbert’s Rock Ventures is an American-based firm, while RFR Holdings LLC has headquarters in New York and Frankfurt. “We can buy something more expensive because we have our own capital, plus European capital that looks for longer returns,” Rosen explained in a recent New York Times interview. “We don’t have to get in and out quickly, and having this long view allows us to be more aggressive.”

Aby Rosen, courtesy of Christopher Peterson via Wikimedia.
RFR’s acquisitions represent a broad trend of foreign investment in American real estate since the late 1980s. In lieu of escrow accounts in Swiss banks and securities in the Caribbean, which have come under intense international scrutiny, foreign investors have poured their money into global real estate, which can serve as a “convenient pied-à-terre, an investment hedge against a wobbly home currency,” according to New York Magazine, “or an insurance policy—a literal refuge if things go bad.” After the U.S. housing crisis from 2007 to 2010, property values in American cities plummeted, and while the U.S. economy has been recovering, they are still relatively “low” compared to cities around the world.
The market rate for luxury apartments in Hong Kong, for instance, is between $4,100 and $5,000 per square foot; in London the same properties are valued at $3,300 to $4,100. By comparison, Manhattan properties cost half that, ranging from about $2,100 to $2,500; alas–well out of reach for even upper middle-class inhabitants, yet quite attractive for transnational ultra-rich investors. Since 2008, roughly 30 percent of condo sales in Manhattan have been to overseas addresses, or through ambiguous entities like limited-liability corporations, such as RFR Holdings LLC, which often serve as middlemen for foreign investors. Over the last decade the majority of New York property sales have gone to investors in Russia or Saudi Arabia; over the last year, however, China has spent $22 billion on New York properties–72 percent more than they spent in 2013–claiming the lion’s share of foreign investment in American real estate. “The global elite,” according to Michael Stern, owner of JDS Development Group, “is basically looking for a safe-deposit box.”
Such gentrification on the global scale should not surprise us–it is a historical trend, and the redevelopment of 190 Bowery was inevitable. But there are dangers to this phenomenon, which reach further than the displacement of middle and working class communities, and erasure of their identity and culture. There is virtually no local market for premium properties in New York City. Urban properties as investments cease to be homes. Foreign investors lack vested interest in maintaining these properties primarily because they do not live there; the American city has effectively become a place of visitors, void of close community ties and stewardship. This hollow space is lifeless. Urban properties as investments are mostly uninhabited by their affluent proprietors; they either serve as vacation homes, or remain empty retainers of wealth. Meanwhile, middle-class homes let rooms to AirBnB, and subdivide apartments as room-shares marketed at exorbitant rates on Craigslist. We are experiencing the emergence of an absentee rentier class that not only augments our urban housing crisis; this urban real-estate bubble may threaten the systemic integrity of our economy.
What needs to change? Buyers of new construction in the city often qualify for significant tax abatements–a vestige of the neoliberal initiatives of the late 1970s and early 1980s designed to increase private investment and reverse the effects of urban crisis. Moreover, entities like RFR, based in Europe with an increasing presence in New York, have capitalized on liberal transnational financial regulations. American cities must update their zoning laws, with an eye to equitable development. New York no longer needs a mainline feed of private investment to remain viable. The effects of unfettered transnational capital currents erode the fabric of urban communities. If “UUGGHH” is not a lament, it is surely an expression of our impotence.







Comments